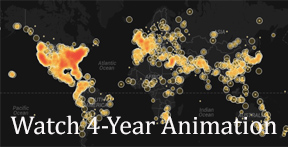
We are excited to unveil a couple experimental data-driven visualizations that literally map 400,000 hours of U.S. television news. One of our collaborating scholars, Kalev Leetaru, applied “fulltext geocoding” software to our entire television news research service collection. These algorithms scan the closed captioning of each broadcast looking for any mention of a location anywhere in the world, disambiguate them using the surrounding discussion (Springfield, Illinois vs Springfield, Massachusetts), and ultimately map each location. The resulting CartoDB visualizations provide what we believe is one of the first large-scale glimpses of the geography of American television news, beginning to reveal which areas receive outsized attention and which are neglected.
Watch TV news mentions of places throughout the world for each day.
Select a TV station and time window to view their representations of places.
Keep in mind that as you explore, zoom-in and click the locations in these pilot maps, you are going to find a lot of errors. Those range from errors in the underlying closed captioning (“two Paris of shoes”) to locations that are paired with onscreen information (a mention of “Springfield” while displaying a map of Massachusetts on the screen). Thus, as you click around, you’re going to find that some locations work great, while others have a lot more error, especially small towns with common names.
What you see here represents our very first experiment with revealing the geography of television news and required bringing together a bunch of cutting-edge technologies that are still very much active areas of research. While there is still lots of work to be done, we think this represents a tremendously exciting prototype for new ways of interacting with the world’s information by organizing it geographically and putting it on a map where it belongs!
Virtual Machines: Unlocking Media for Research
In addition to our public web-based research service, we are facilitating scholars, like Kalev, and other researchers in applying advanced data treatments to our entire collection, at a speed and scale beyond any individual’s capacity. As responsible custodians of an enormous collection of television news content created by others, we endeavor to secure their work within the context of our library. Therefore, rather than lending out copies of large portions of the collection for study, researchers instead work in our “virtual reading room” where they may run their computer algorithms on our servers within the physical confines of the Archive. We hope our evolving demonstrations of this data queries in — results out — process may help forge a new model for how exceptional public interest value can be derived from media without challenging their value and integrity to their creators.
The Knight Foundation and other insightful donors are providing critical support in our ongoing efforts to open television news and join with others in re-visioning how digital libraries can respectfully address the educational potential of other diverse media. We hope you will consider lending your support.