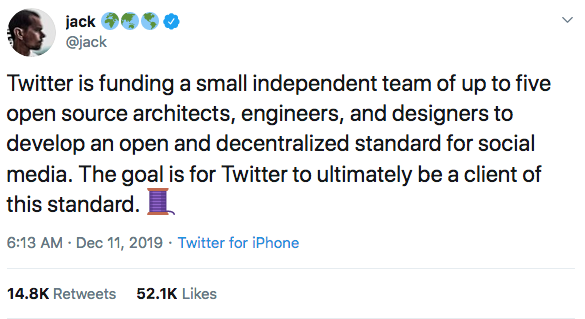
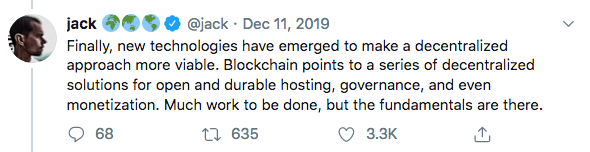
The pending sale of Twitter to Elon Musk has generated a buzz about the future of social media and just who should control our data.
Wendy Hanamura, director of partnerships at the Internet Archive, moderated an online discussion April 28 “Goodbye Facebook, Hello Decentralized Social Media?” about the opportunities and dangers ahead. The webinar is part of a series of six workshops, “Imagining a Better Online World: Exploring the Decentralized Web.”
Watch the session recording:
The session featured founders of some of the top decentralized social media networks including Jay Graber, chief executive officer of R&D project Bluesky, Matthew Hodgson, technical co-founder of Matrix, and Andre Staltz, creator of Manyverse. Unlike Twitter, Facebook or Slack, Matrix and Manyverse have no central controlling entity. Instead the peer-to-peer networks shift power to the users and protect privacy.
If Twitter is indeed bought and people are disappointed with the changes, the speakers expressed hope that the public will consider other social networks. “A crisis of this type means that people start installing Manyverse and other alternatives,” Staltz said. “The opportunity side is clear.” Still in the transition period if other platforms are not ready, there is some risk that users will feel stuck and not switch, he added.
Hodgson said there are reasons to be both optimistic and pessimistic about Musk purchasing Twitter. The hope is that he will use his powers for good, making it available to everybody and empowering people to block the content they don’t want to see. The risk is with no moderation, Hodgson said, people will be obnoxious to one another without sufficient controls to filter, and the system will melt down. “It’s certainly got potential to be an experiment. I’m cautiously optimistic on it,” he said.
People who work in decentralized tech recognize the risk that comes when one person can control a network and act for good or bad, Graber said. “This turn of events demonstrates that social networks that are centralized can change very quickly,” she said. “Those changes can potentially disrupt or drastically alter people’s identity, relationships, and the content that they put on there over the years. This highlights the necessity for transition to a protocol-based ecosystem.”
When a platform is user-controlled, it is resilient to disruptive change, Graber said. Decentralization enables immutability so change is hard and is a slow process that requires a lot of people to agree, added Staltz.
The three leaders spoke about how decentralized networks provide a sustainable alternative and are gaining traction. Unlike major players that own user data and monetize personal information, decentralized networks are controlled by users and information lives in many different places.
“Society as a whole is facing a lot of crises,” Graber said. “We have the ability to, as a collective intelligence, to investigate a lot of directions at once. But we don’t actually have the free ability to fully do this in our current social architecture…if you decentralize, you get the ability to innovate and explore many more directions at once. And all the parts get more freedom and autonomy.”
Decentralized social media is structured to change the balance of power, added Hanamura: “In this moment, we want you to know that you have the power. You can take back the power, but you have to understand it and understand your responsibility.”
The webinar was co-sponsored by DWeb and Library Futures, and presented by the Metropolitan New York Library Council (METRO).
The next event in the series, Decentralized Apps, the Metaverse and the “Next Big Thing,” will be held Thursday, May 26 at 4-5 p.m.EST, Register here