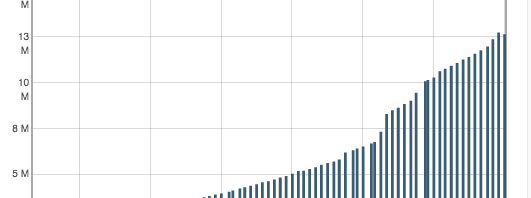
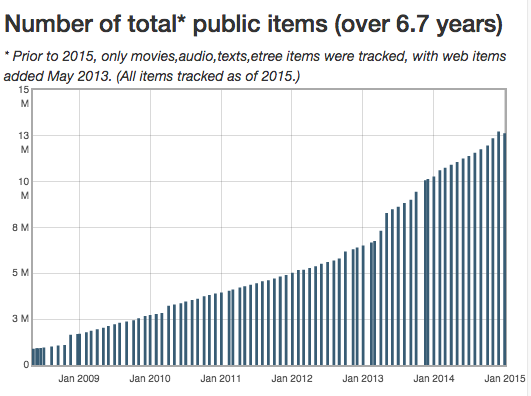
Every month, we look over the total download counts for all public items at archive.org. We sum item counts into their collections. At year end 2014, we found various source reliability issues, as well as overcounting for “top collections” and many other issues.
To address the problems we did:
- Rebuilt a new system to use our database (DB) for item download counts, instead of our less reliable (and more prone to “drift”) SOLR search engine (SE).
- Changed monthly saved data from JSON and PHP serialized flatfiles to new DB table — much easier to use now!
- Fixed overcounting issues for collections: texts, audio, etree, movies
- Fixed various overcounting issues related to not unique-ing <collection> and <contributor> tags (more below)
- Fixes to character encoding issues on <contributor> tags
Bonus points!
- We now track *all collections*. Previously, we only tracked items tagged:
- <mediatype> texts
- <mediatype> etree
- <mediatype> audio
- <mediatype> movies
- For items we are tracking <contributor> tags (texts items), we now have a “Contributor page” that shows a table of historical data.
- Graphs are now “responsive” (scale in width based on browser/mobile width)
The Overcount Issue for top collection/mediatypes
- In the below graph, mediatypes and collections are shown horizontally, with a sample “collection hierarchy” today.
- For each collection/mediatype, we show 1 example item, A B C and D, with a downloads/streams/views count next to it parenthetically. So these are four items, spanning four collections, that happen to be in a collection hierarchy (a single item can belong to multiple collections at archive.org)
- The Old Way had a critical flaw — it summed all sub-collection counts — when really it should have just summed all *direct child* sub-collection counts (or gone with our New Way instead)
So we now treat <mediatype> tags like <collection> tags, in terms of counting, and unique all <collection> tags to avoid items w/ minor nonideal data tags and another kind of overcounting.
… and one more update from Feb/1:
We graph the “difference” between absolute downloads counts for the current month minus the prior month, for each month we have data for. This gives us graphs that show downloads/month over time. However, values can easily go *negative* with various scenarios (which is *wickedly* confusing to our poor users!)
Here’s that situation:
A collection has a really *hot* item one month, racking up downloads in a given collection. The next month, a DMCA takedown or otherwise removes the item from being available (and thus counted in the future). The downloads for that collection can plummet the next month’s run when the counts are summed over public items for that collection again. So that collection would have a negative (net) downloads count change for this next month!
Here’s our fix:
Use the current month’s collection “item membership” list for current month *and* prior month. Sum counts for all those items for both months, and make the graphed difference be that difference. In just about every situation that remains, graphed monthly download counts will be monotonic (nonnegative and increasing or zero).