- Which recent hurricane got the least amount of attention from TV news broadcasters?
- Irma
- Maria
- Harvey
- Thomas Jefferson said, “Government that governs least governs best.”
- True
- False
- Mitch McConnell shows up most on which cable TV news channel?
- CNN
- Fox News
- MSNBC
Answers at end of post.

The Internet Archive’s TV News Archive, our constantly growing online, free library of TV news broadcasts, contains 1.4 million shows, some dating back to 2009, searchable by closed captioning. History is happening, and we preserve how broadcast news filters it to us, the audience, whether it’s through CNN’s Jake Tapper, Fox’s Bill O’Reilly, MSNBC’s Rachel Maddow or others. This archive becomes a rich resource for journalists, academics, and the general public to explore the biases embedded in news coverage and to hold public officials accountable.
Last October we wrote how the Internet Archive’s TV News Archive was “hacking the election,” then 13 days away. In the year since, we’ve been applying our experience using machine learning to track political ads and TV news coverage in the 2016 elections to experiment with new collaborations and tools to create more ways to analyze the news.

Helping fact-checkers
Since we launched our Trump Archive in January 2017, and followed in August with the four congressional leaders, Democrat and Republican, as well as key executive branch figures, we’ve collected some 4,534 hours of curated programming and more than 1,300 fact-checks of material on subjects ranging from immigration to the environment to elections.
The 1,340 fact-checks–and counting–represent a subset of the work of partners FactCheck.org, PolitiFact and The Washington Post’s Fact Checker, as we link only to fact-checks that correspond to statements that appear on TV news. Most of the fact-checks–524–come from PolitiFact; 492 are by FactCheck.org, and 324 from The Washington Post’s Fact Checker.
We’re also proud to be part of the Duke Reporter’s Lab’s new Tech & Check collaborative, where we’re working with journalists and computer scientists to develop ways to automate parts of the fact-checking process. For example, we’re creating processes to help identify important factual claims within TV news broadcasts to help guide fact-checkers where to concentrate their efforts. The initiative received $1.2 million from the John S. and James L. Knight Foundation, the Facebook Journalism Project and the Craig Newmark Foundation.
See the Trump, US Congress, and executive branch archives and collected fact-checks.
TV News Kitchen
We’re collaborating with data scientists, private companies and nonprofit organizations, journalists, and others to cook up new experiments available in our TV News Kitchen, providing new ways to analyze TV news content and understand ourselves.
Dan Schultz, our senior creative technologist, worked with the start-up Matroid to develop Face-o-Matic, which tracks faces of selected high level elected officials on major TV cable news channels: CNN, Fox News, MSNBC, and BBC News. The underlying data are available for download here. Unlike caption-based searches, Face-o-Matic uses facial recognition algorithms to recognize individuals on TV news screens. It is sensitive enough to catch this tiny, dark image of House Minority Leader Nancy Pelosi, D., Calif., within a graphic, and this quick flash of Senate Minority Leader Chuck Schumer, D., N.Y., and Senate Majority Leader Mitch McConnell, R., Ky.
The work of TV Architect Tracey Jaquith, our Third Eye project scans the lower thirds of TV screens, using OCR, or optical character recognition, to turn these fleeting missives into downloadable data ripe for analysis. Launched in September 2017, Third Eye tracks BBC News, CNN, Fox News, and MSNBC, and collected more than four million chyrons captured in just over two weeks, and counting.
Download Third Eye data. API and TSV options available.
Vox news reporter Alvin Chang used the Third Eye chyron data to report how Fox News paid less attention to Hurricane Maria’s destruction in Puerto Rico than it did to Hurricanes Irma and Harvey, which battered Florida and Texas. Chang’s work followed a similar piece by Dhrumil Mehta for FiveThirtyEight, which used Television Explorer, a tool developed by data scientist Kalev Leetaru to search and visualize closed captioning on the TV News Archive.
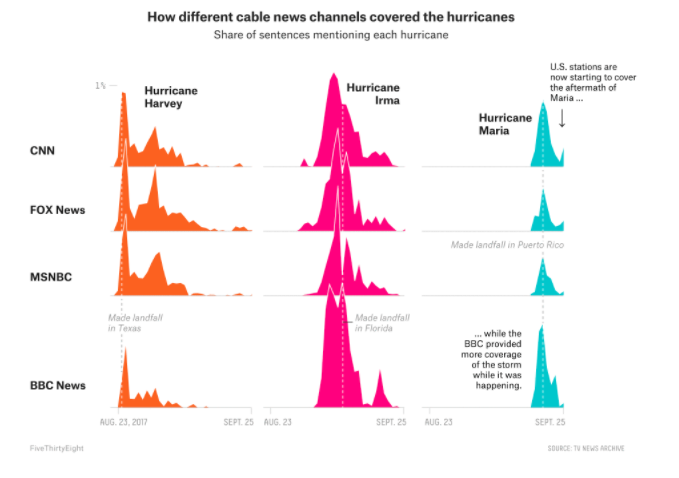
FiveThirtyEight used TV News Archive captions to create this look at how cable networks covered recent hurricanes.
CNN’s Brian Stelter followed up with a similar analysis on “Reliable Sources” October 1.
We’re also working with academics who are using our tools to unlock new insights. For example, Schultz and Jaquith are working with Bryce Dietrich at the University of Iowa to apply the Duplitron, the audiofingerprinting tool that fueled our political ad airing data, to analyze floor speeches of members of Congress. The study identifies which floor speeches were aired on cable news programs and explores the reasons why those particular clips were selected for airing. A draft of the paper was presented in the 2017 Polinfomatics Workshop in Seattle and will begin review for publication in the coming months.
What’s next? Our plans include making more than a million hours of TV news available to researchers from both private and public institutions via a digital public library branch of the Internet Archive’s TV News Archive. These branches would be housed in computing environments, where networked computers provide the processing power needed to analyze large amounts of data. Researchers will be able to conduct their own experiments using machine learning to extract metadata from TV news. Such metadata could include, for example, speaker identification–a way to identify not just when a speaker appears on a screen, but when she or he is talking. Metadata generated through these experiments would then be used to enrich the TV News Archive, so that any member of the public could do increasingly sophisticated searches.
Going global
We live in an interdependent world, but we often lack understanding about how other cultures perceive us. Collecting global TV could open a new window for journalists and researchers seeking to understand how political and policy messages are reported and spread across the globe. The same tools we’ve developed to track political ads, faces, chyrons, and captions can help us put news coverage from around the globe into perspective.
We’re beginning work to expand our TV collection to include more channels from around the globe. We’ve added the BBC and recently began collecting Deutsche Welle from Germany and the English-language Al Jazeera. We’re talking to potential partners and developing strategy about where it’s important to collect TV and how we can do so efficiently.
History is happening, but we’re not just watching. We’re collecting, making it accessible, and working with others to find new ways to understand it. Stay tuned. Email us at tvnews@archive.org. Follow us @tvnewsarchive, and subscribe to our weekly newsletter here.
Answer Key
- b. (See: “The Media Really Has Neglected Puerto Rico,” FiveThirtyEight.
- b. False. (See: Vice President Mike Pence statement and linked PolitiFact fact-check.)
- c. MSNBC. (See: Face-O-Matic blog post.)
Members of the TV News Archive team: Roger Macdonald, director; Robin Chin, Katie Dahl, Tracey Jaquith, Dan Schultz, and Nancy Watzman.