Watching a single episode of the evening news can be informative. Tracking trends in broadcasts over time can be fascinating.
The Internet Archive has preserved nearly 3 million hours of U.S. local and national TV news shows and made the material open to researchers for exploration and non-consumptive computational analysis. At a webinar April 13, TV News Archive experts shared how they’ve curated the massive collection and leveraged technology so scholars, journalists and the general public can make use of the vast repository.
Roger Macdonald, founder of the TV News Archive, and Kalev Leetaru, collaborating data scientist and GDELT Project founder, spoke at the session. Chris Freeland, director of Open Libraries, served as moderator and Internet Archive founder Brewster Kahle offered opening remarks.
Watch video
“Growing up in the television age, [television] is such an influential, important medium—persuasive, yet not something you can really quote,” Kahle said. “We wanted to make it so that you could quote, compare and contrast.”
The Internet Archive built on the work of the Vanderbilt Television Archive, and the UCLA Library Broadcast NewsScape to give the public a broader “macro view,” said Kahle. The trends seen in at-scale computational analyses of news broadcasts can be used to understand the bigger picture of what is happening in the world and the lenses through which we see the world around us.
In 2012, with donations from individuals and philanthropies such as the Knight Foundation, the Archive started repurposing the closed captioning data stream required of all U.S. broadcasters into a search index. “This simple approach transformed the antiquated experience of searching for specific topics within video,” said Macdonald, who helped lead the effort. “The TV caption search enabled discovery at internet speed with the ability to simultaneously search millions of programs and have your results plotted over time, down to individual broadcasters and programs.”
“[Television] is such an influential, important medium—persuasive, yet not something you can really quote. We wanted to make it so that you could quote, compare and contrast.”
Brewster Kahle, Internet Archive
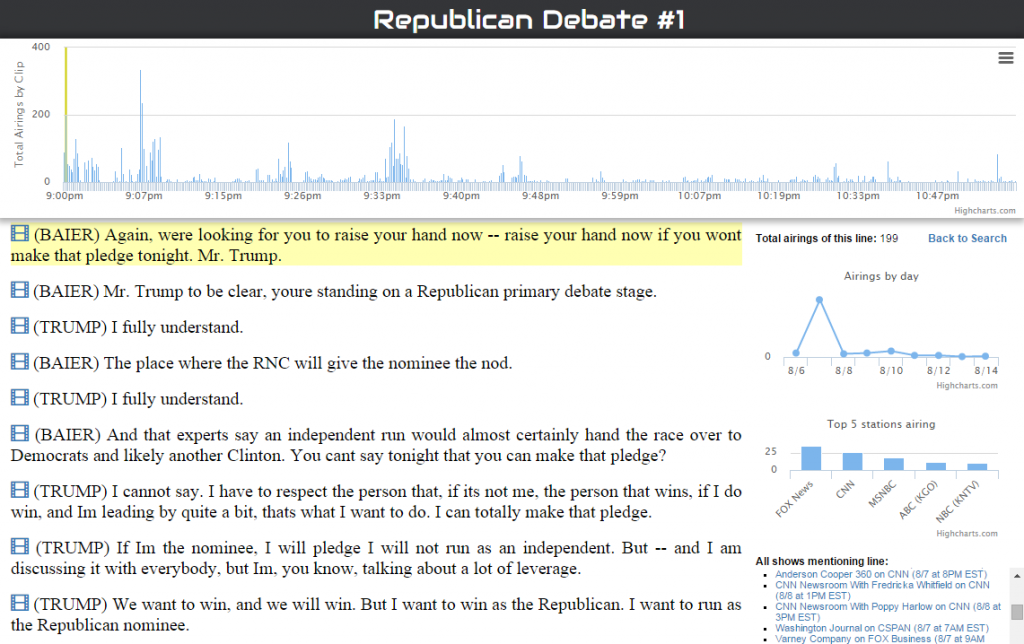
Scholars and journalists were quick to embrace this opportunity, but the team kept experimenting with deeper indexing. Techniques like audio fingerprinting, Optical Character Recognition (OCR) and Computer Vision made it possible to capture visual elements of the news and improve access, Macdonald said.
Sub-collections of political leaders’ speeches and interviews have been created, including an extensive Donald Trump Archive. Some of the Archive’s most productive advances have come from collaborating with outsiders who have requested more access to the collection than is available through the public interface, Macdonald said. With appropriate restrictions to maintain respect for broadcasters and distribution platforms, the Archive has worked with select scientists and journalists as partners to use data in the collection for more complex analyses.
Treating television as data
Treating television news as data creates vast opportunities for computational analysis, said Leetaru. Researchers can track word frequency use in the news and how that has changed over time. For instance, it’s possible to look at mentions of COVID-related words across selected news programs and see when it surged and leveled off with each wave before plummeting downward, as shown in the graph below.
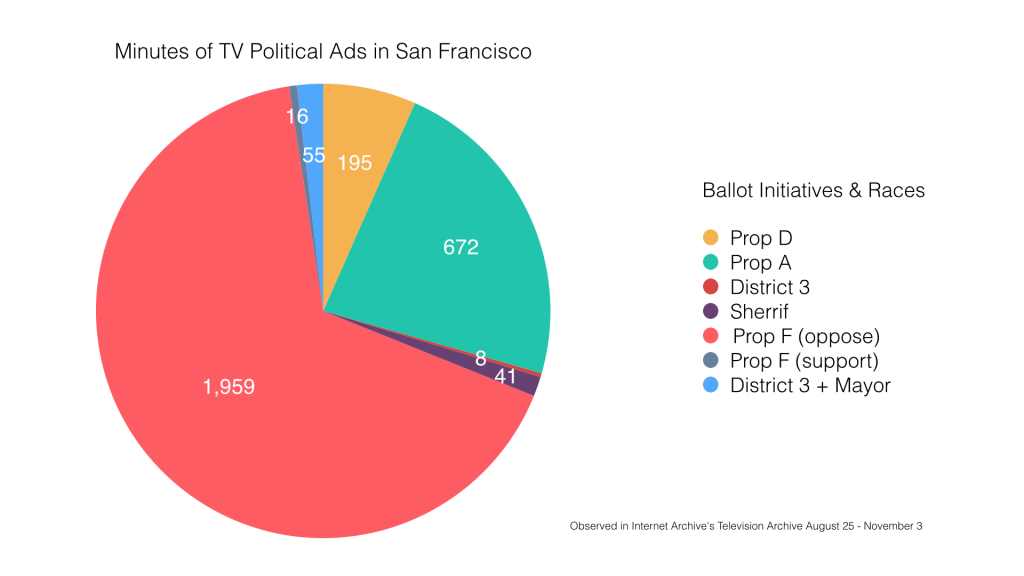
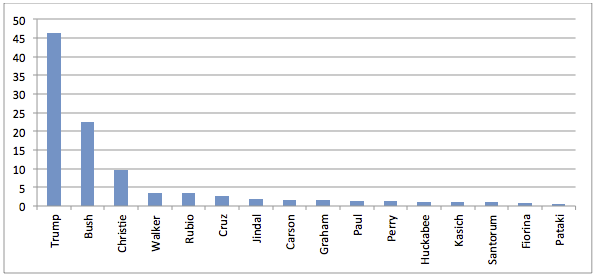
The newly computed metadata can help provide context and assist with fact checking efforts to combat misinformation. It can allow researchers to map the geography of television news—how certain parts of the world are covered more than others, Leetaru said. Through the collections, researchers have explored which presidential tweets challenging election integrity got the most exposure on the news. OCR of every frame has been used to create models of how to identify names of every “Dr.” depicted on cable TV after the outbreak of COVID-19 and calculate air time devoted to the medical doctors commenting on one of the virus variants. Reverse image lookup of images in TV news has been used to determine the source of photos and videos. Visual entity search tools can even reveal the increasing prevalence of bookshelves as backdrops during home interviews in the pandemic, as well as appearances of books by specific authors or titles. Open datasets of computed TV news metadata are available that include all visual entity and OCR detections, 10-minute interval captioning ngrams and second by second inventories of each broadcast cataloging whether it was “News” programming, “Advertising” programming or “Uncaptioned” (in the case of television news this is almost exclusively advertising).
From television news to digitized books and periodicals, dozens of projects rely on the collections available at archive.org for computational and bibliographic research across a large digital corpus. Data scientists or anyone with questions about the TV News Archives, can contact info@archive.org.
Up Next
This webinar was the fourth a series of six sessions highlighting how researchers in the humanities use the Internet Archive. The next will be about Analyzing Biodiversity Literature at Scale on April 27. Register here.